Welcome to Shihua Zhang's Lab
Bioinformatics and Data Science
Software:
|
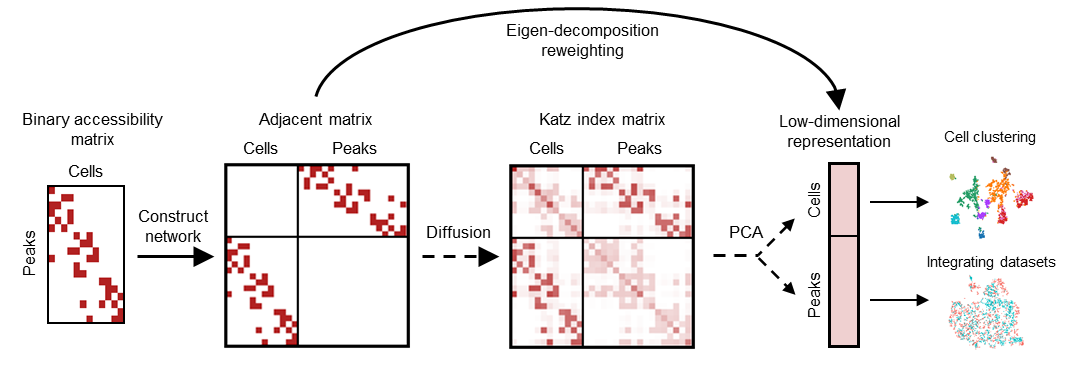
scAND (scATAC-seq data Analysis via Network Diffusion) is a python-based package for scalable embedding of massive scATAC-seq data. scAND treats peaks-by-cells matrix as a bipartite network that indicates the accessible relationship between cells and peaks and employs a network diffusion method to alleviate the data sparsity and gather the global information. scAND improves the clustering performance on both simulated and real datasets, and can be applied to data integration.
[scAND_Guide]
|
|
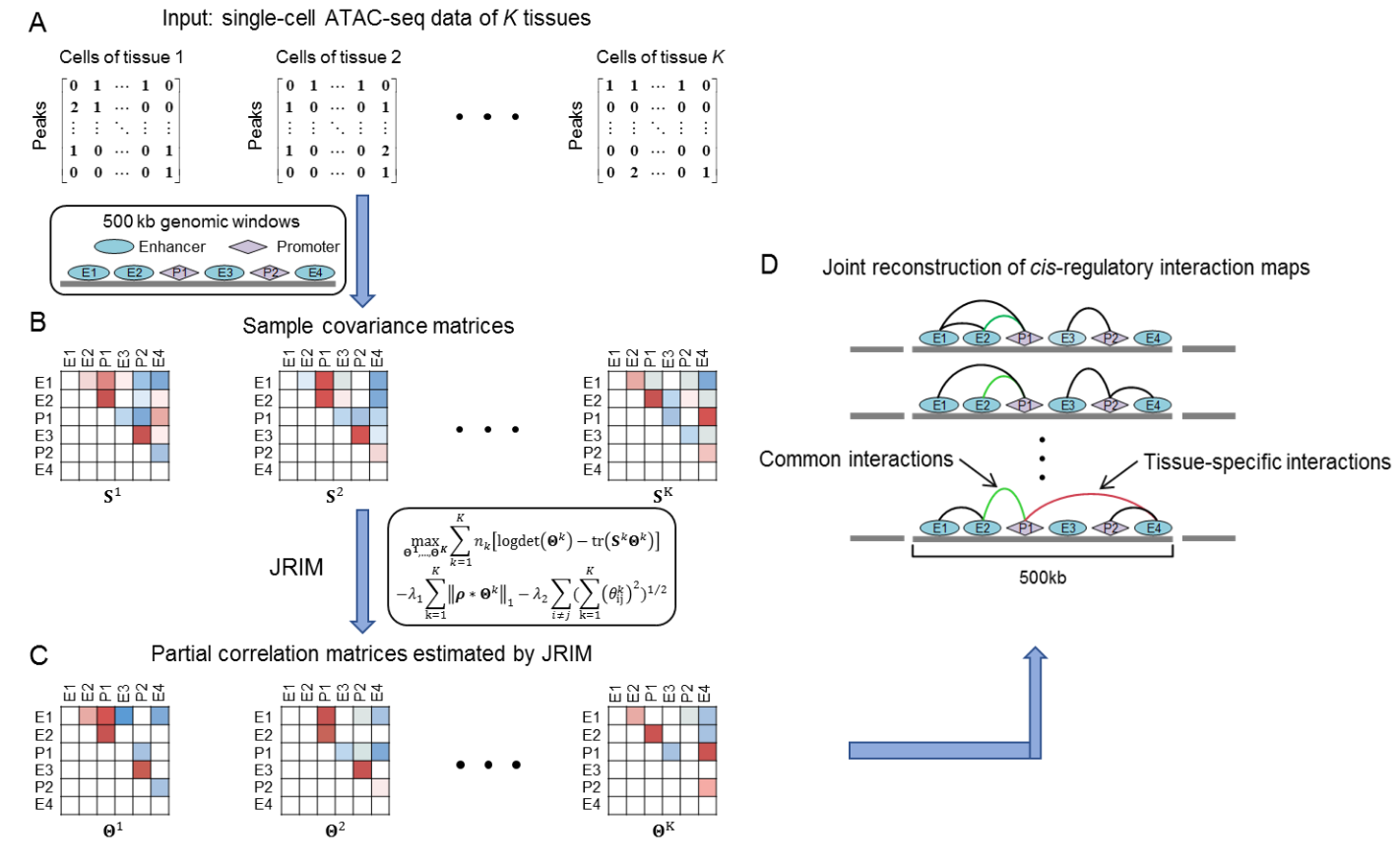
JRIM is a package for Jointly Reconstructing cis-regulatory Interaction Maps of multiple cell populations using single-cell chromatin
accessibility data and identifying shared and common interaction patterns. It uses an aggregation process to deal with the sparsity of single-cell data,
exploits similarity between cell types via a group lasso penalty, and generates comparable networks.
JRIM could be used to characterize difference between cell types or identify dynamic changes during cell development.
[JRIM_Guide]
|
|
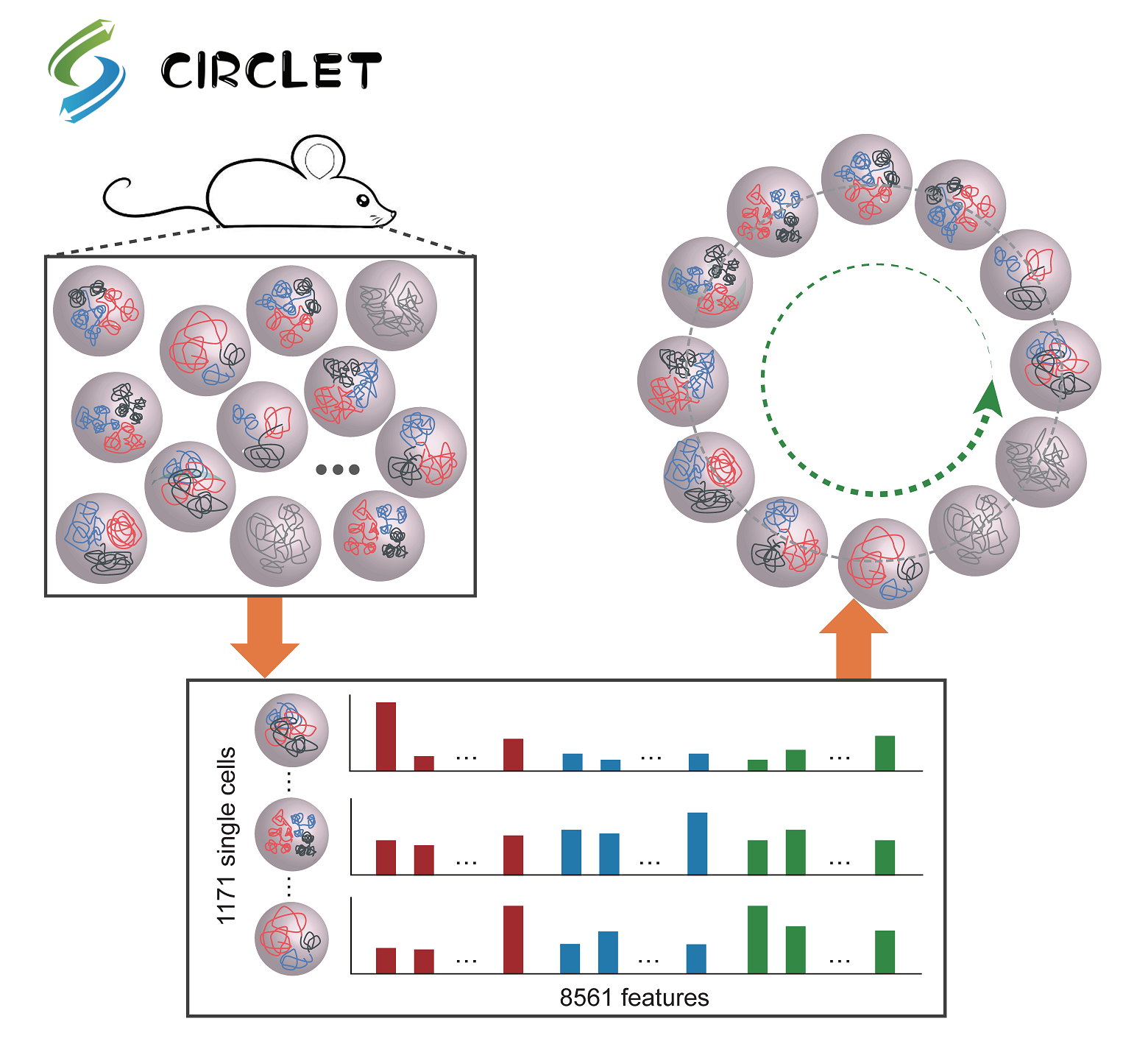
CIRCLET, a powerful tool for accurate reconstruction of circular trajectory with high resolution by
considering multi-scale features of chromosomal architectures of single cells. Further division of
the reconstructed trajectory helps to accurately characterize the dynamics of chromosomal structures
and uncover important regulatory genes along cell-cycle progression, providing a novel framework for
discovering regulatory regions even cancer markers at single-cell resolution.
[Guide]
|
|
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data analysis remains challenging due to the presence of dropout events (i.e., excess zero counts).
Taking account of cell heterogeneity and expression effect on dropout, we propose PBLR to accurately impute the dropouts of scRNA-seq data.
PBLR is an effective tool to recover dropout events on both simulated and real datasets,and can dramatically improve low-dimensional representation and reveal
gene-gene relationship compared to several state-of-the-art methods.
|
|
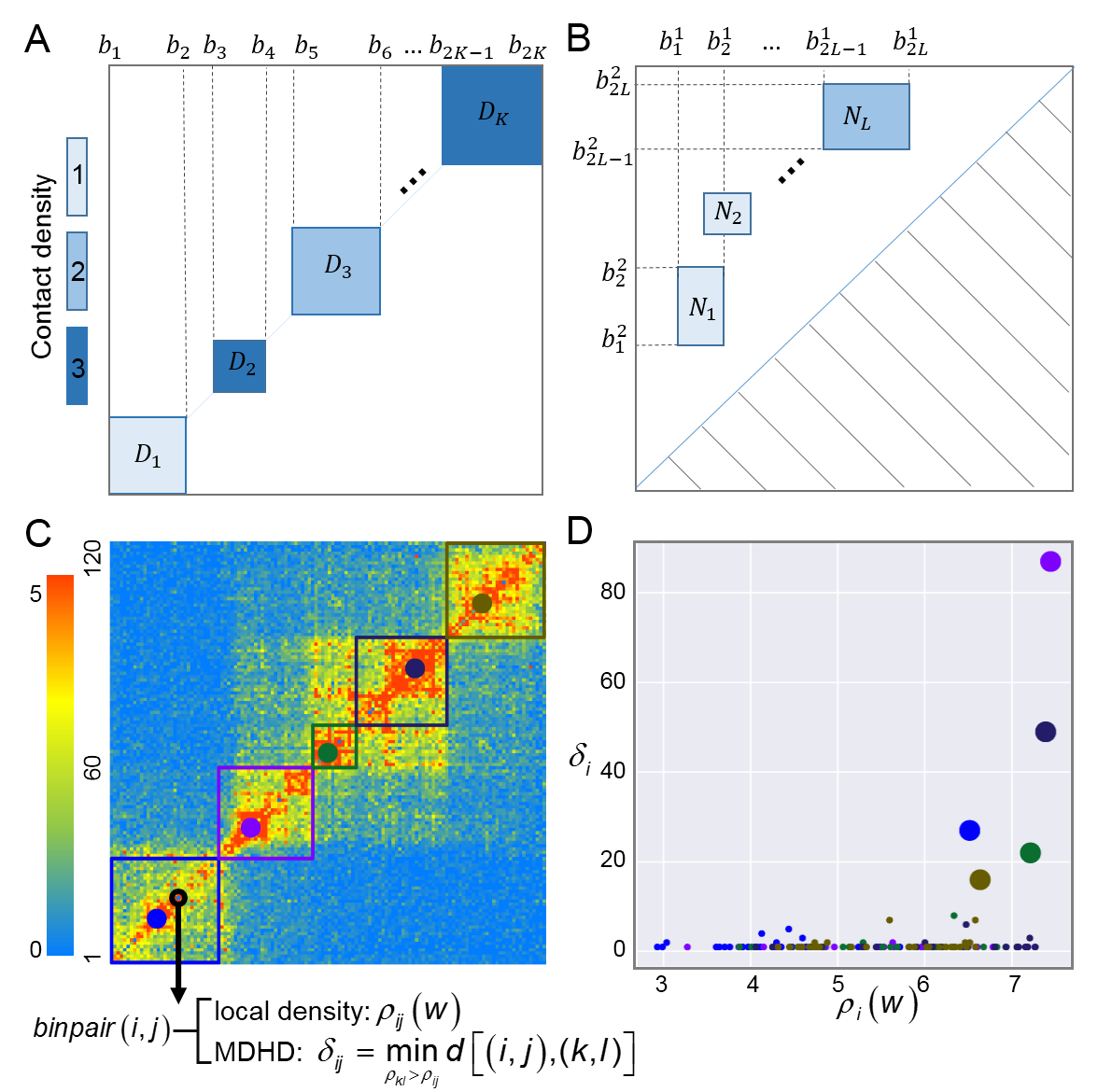
MSTD is a generic and efficient method to identify multi-scale topological domains (MSTD)
from symmetric Hi-C and other high resolution asymmetric promoter capture Hi-C datasets.
[Guide]
|
|
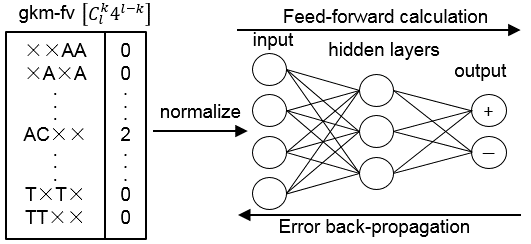
gkm-DNN (gapped k-mer deep neural network) is a software which uses gapped k-mer frequency vector (gkm-fv) as input to train neural networks.
gkm-DNN is designed for classification but can be easily extended to other problems such as regression and ranking. The software is open sourced.
gkm-DNN consists of calculating gkm-fv (using R) and training the neural networks (using Java + DL4J). For more information please see user guide.
[Guide]
|
|
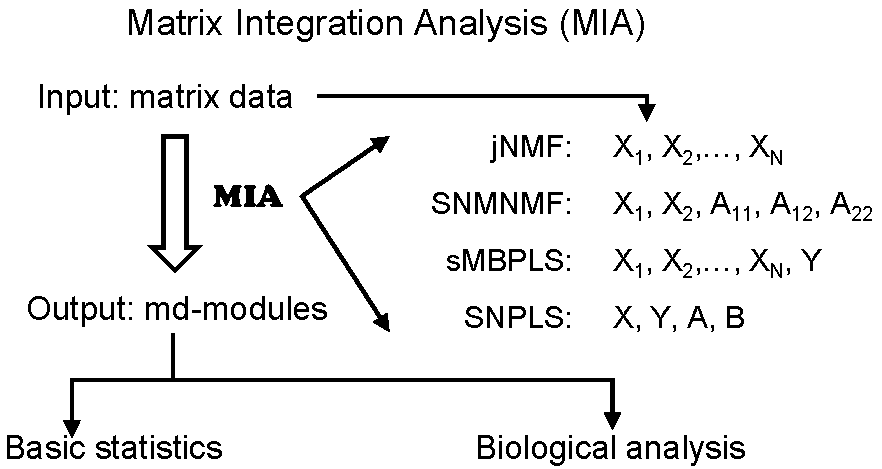
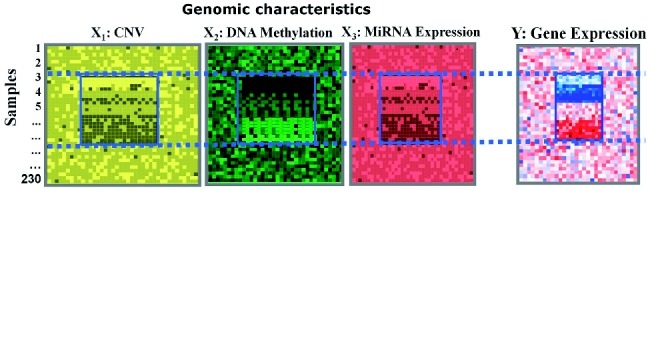
MIA (Matrix Integration Analysis) is a MATLAB package, implementing
and extending four computational methods (Guide). MIA can integrate diverse types of
genomic data (e.g., copy number variation, DNA methylation, gene expression, microRNA
expression profiles and/or gene network data) to identify the underlying modular patterns.
MIA is flexible and can handle a wide range of biological problems and data types.
In addition, MIA can also be run for users without a MATLAB license.
[Guide]
|
|
MDPFinder (Mutated Driver Pathway Finder) is a package
for identifying driver pathways promoting cancer
proliferation and filtering out the unfunctional and
passenger ones. It includes two methods to solve the
so-called Maximum Weight Submatrix problem which is
designed to de novo identify mutated driver pathways
from mutation data in cancer. The first one is an exact
method which can be helpful for assessing other approximate
or/and heuristic algorithms. The second one is a stochastic and
flexible method which can be employed to incorporate other types
of information to improve the first method. [Pubmed]
|
|
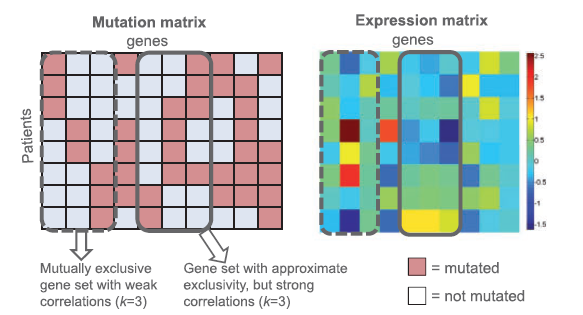
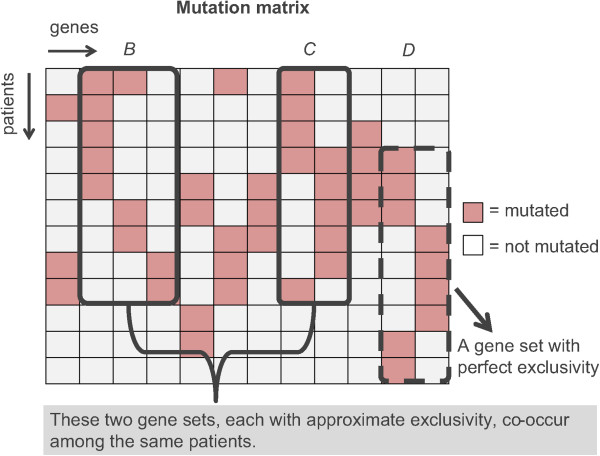
CoMDP (Co-occurring Mutated Driver Pathway) is a package
for de novo identifying co-occurring driver pathways in cancer with mutation data.
The modified version mod_CoMDP can be used to model the situation where a certain
pathway has been previously proven to play important roles in some cancers and one
wants to know whether there are other pathways with cooperative
effects with it. [Pubmed]
|
|
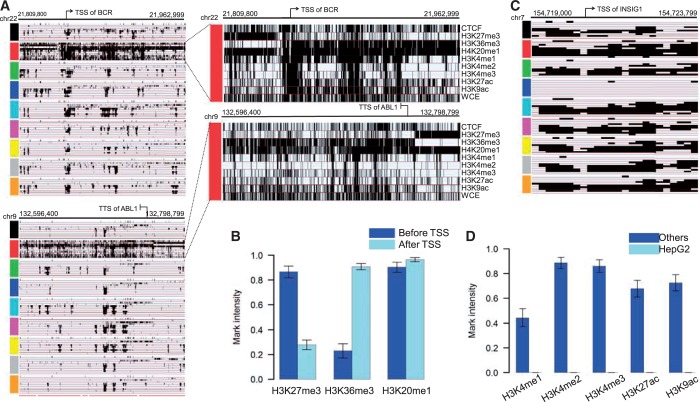
dCMA (differential Chromatin Modification Analysis)
is a package for identifying cell-type specific genomic regions with distinctive
chromatin modifications. It can find cell-type specific elements which are unique
to a cell type investigated. This differential comparative epigenomic strategy
is a promising tool in deciphering the human genome and characterizing cell
specificity. [Pubmed]
|
|
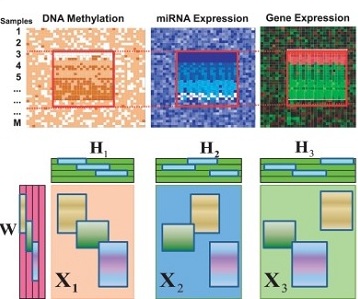
jNMF is a package which implemented the
joint matrix factorization technique to
integrating multi-dimensional genomics
data for the discovery of combinatorial
patterns. It projects multiple types of
genomic data onto a common coordinate system,
in which heterogeneous variables weighted highly
in the same projected direction form a multi-dimensional
module (md-module). Genomic variables in such modules
are characterized by significant correlations and likely
functional associations. [Pubmed]
|
|
sMBPLS (sparse Multi-Block Partial Least Squares) is a package
to identify multi-dimensional regulatory modules from multiple
datasets in a regression manner. A multi-dimensional regulatory
module contains sets of regulatory factors from different layers
that are likely to jointly contribute to a local
"gene expression factory". [Pubmed]
|
|
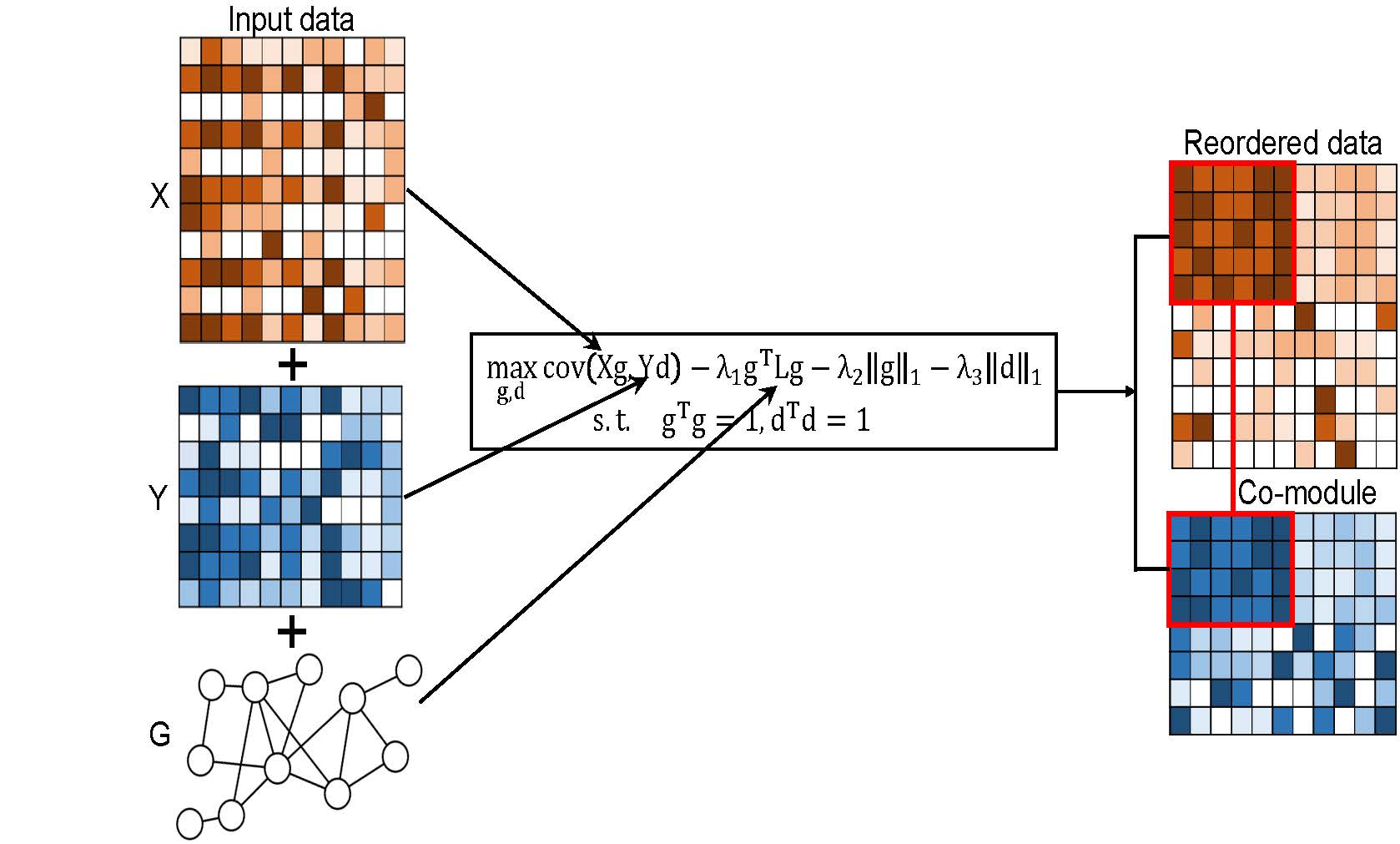
SNPLS (Sparse Network-regularized Partial Least Squares) is a package
to integrate pairwise gene expression and drug response data as well
as a gene interaction network for identifying joint gene-drug
co-modules in a regression manner. This package can be easily adapted
to other biological pairwise data. [Pubmed]
|
|
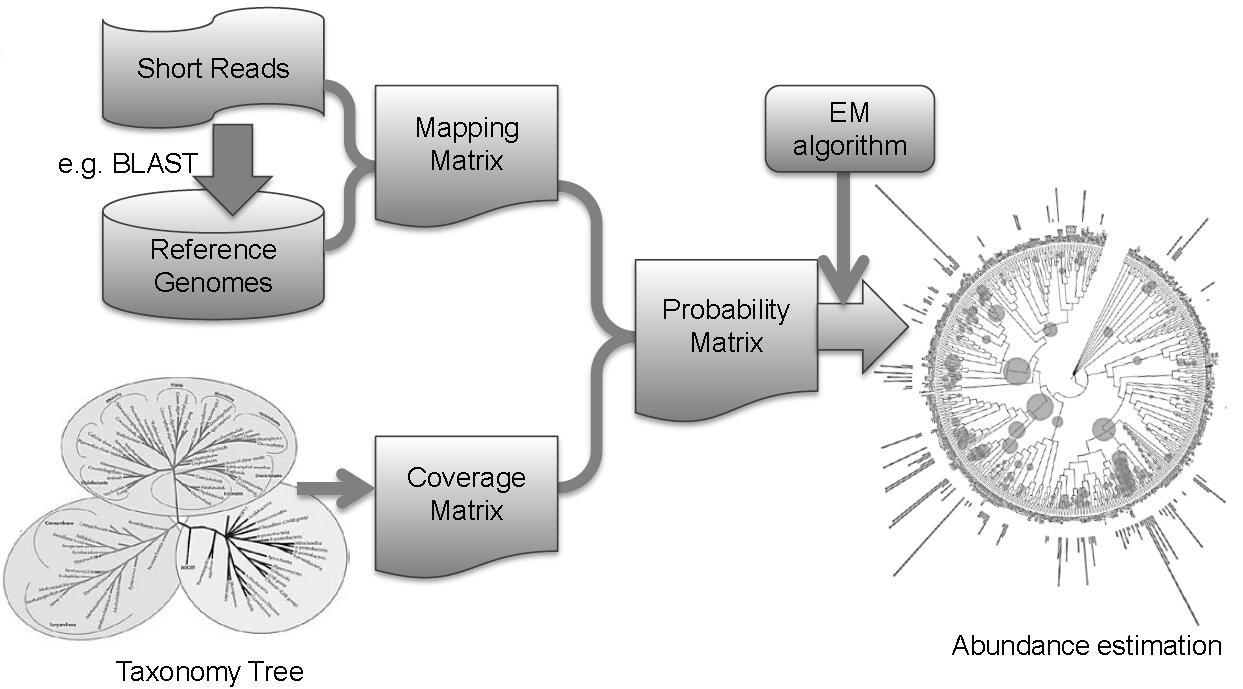
HTTMM (Hierarchical Taxonomy Tree based Mixture Model) is a package designed for
estimating the abundance of taxon within a microbial community by incorporating
the structure of the taxonomy tree. In this model, genome specific short reads and
homologous short reads among genomes can be distinguished and represented by leaf
and intermediate nodes in the taxonomy tree respectively. An expectation-
maximization algorithm has been adopted to solve this model. [Pubmed]
|
|
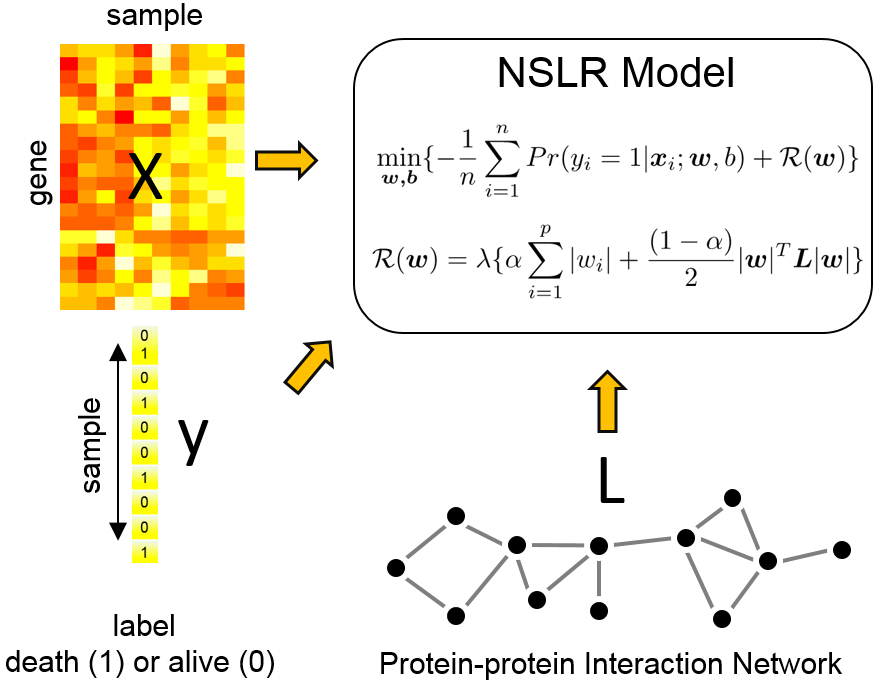
NSLR (Network-regularized Sparse Logistic Regression) is a package to integrate gene expression data,
clinical binary outcome, and normalized Laplacian matrix encoding the protein-protein interaction (PPI)
network for clinical risk prediction and biomarker discovery.
[Guide]
|
|
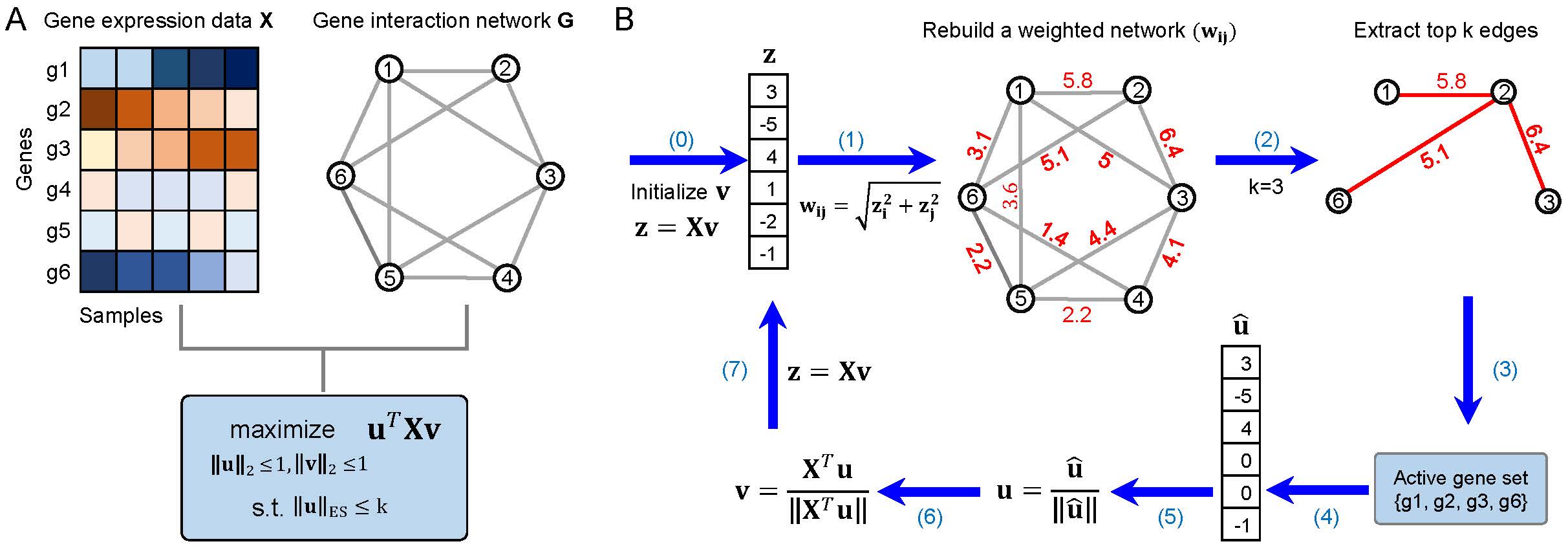
ESPCA (Edge-group Sparse PCA) is a package to integrate the group structure from a prior gene network into the PCA framework for dimension reduction and feature interpretation.
ESPCA enforces sparsity of principal component (PC) loadings through considering the connectivity of gene variables in the prior network. Based on such prior knowledge,
ESPCA can overcome the drawbacks of sparse PCA and capture some gene modules with better biological interpretations.
We also extended ESPCA for analyzing multiple gene expression matrices simultaneously.
[Guide]
|
|
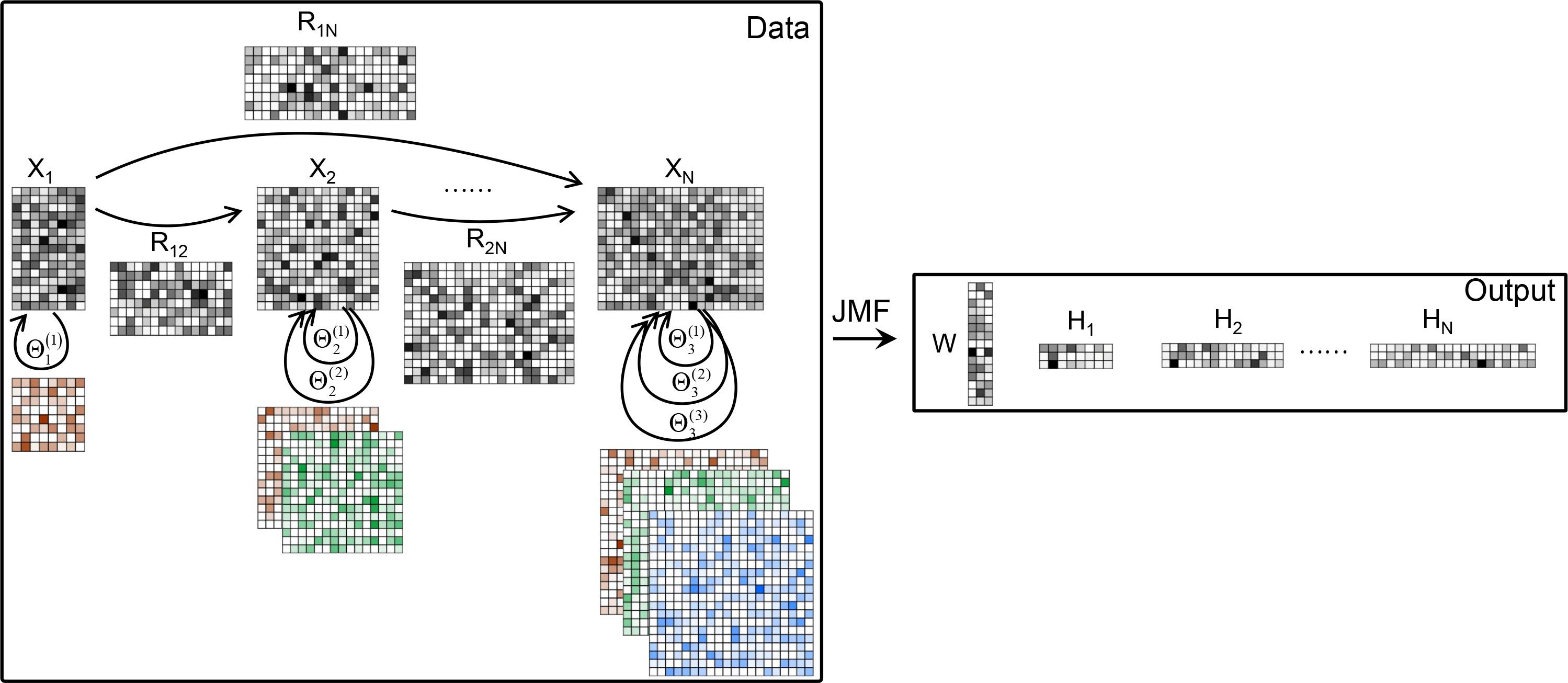
JMF (Joint Matrix Factorization) is a MATLAB package to integrate multi-view data as well as prior relationship knowledge within or between multi-view data for pattern recognition and data mining.
Four update rules are adopted for solving JMF. Additionally, two adapted prediction JMF models based on JMF are provided.
[Guide]
|
|
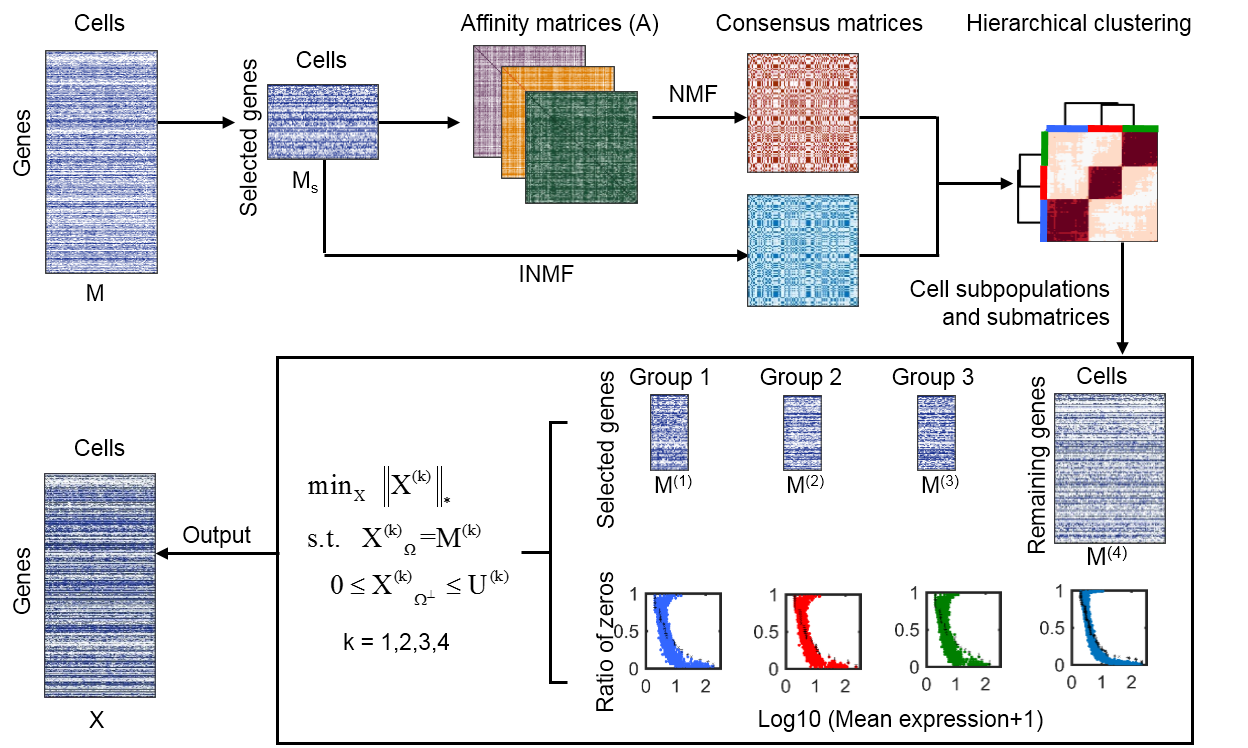
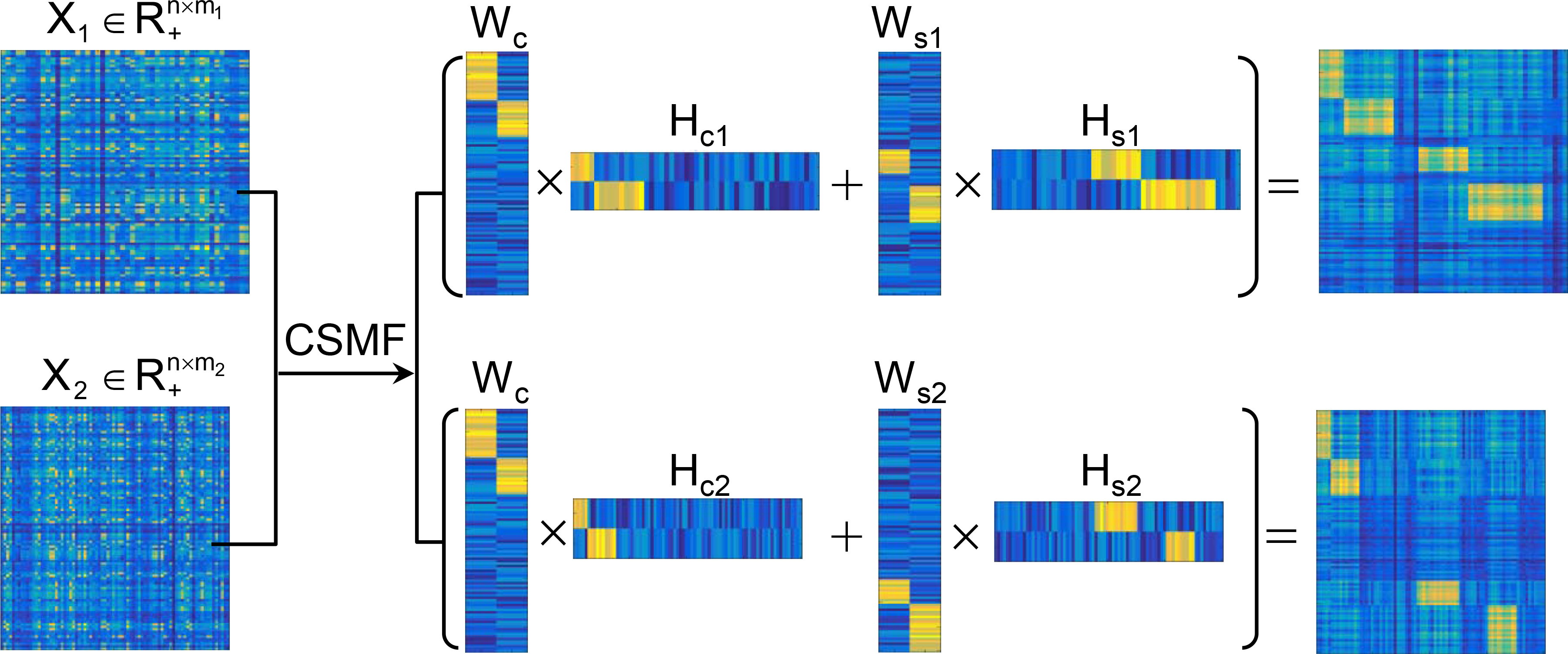
CSMF (Common and Specific Matrix Factorization) is a MATLAB package to simultaneously extract common and specific patterns from the data of two or multiple biological
interrelated conditions via matrix factorization. In addition to the main functions, this package also includes data simulation, parameter selection, solution fine tuning, etc.
CSMF can be widely used to analyze various data types such as RNA-seq, Chip-seq and scRNA-seq.
[Guide]
[CSMF_tutorial]
|